Ingress
Ingress exposes HTTP and HTTPS routes from outside the cluster to services within the cluster. Traffic routing is controlled by rules defined on the Ingress resource.
Prerequisites
Before you create an Ingress, you need to have the following:
- An installed Ingress Controller in your cluster. SkyU supports NGINX and Traefik Ingress Controllers. You can install the Ingress Controller by following the instructions in the Ingress Controller section.
- DNS records for the domain you want to use for the Ingress. You can register a wildcard or a DNS in SkyU Clusters. Read more in Cluster DNS section.
- Cert Manager installed in your cluster if you want to use cert-manager certificates. You can install cert-manager by following the instructions in the Cert Manager section.
Create Ingress
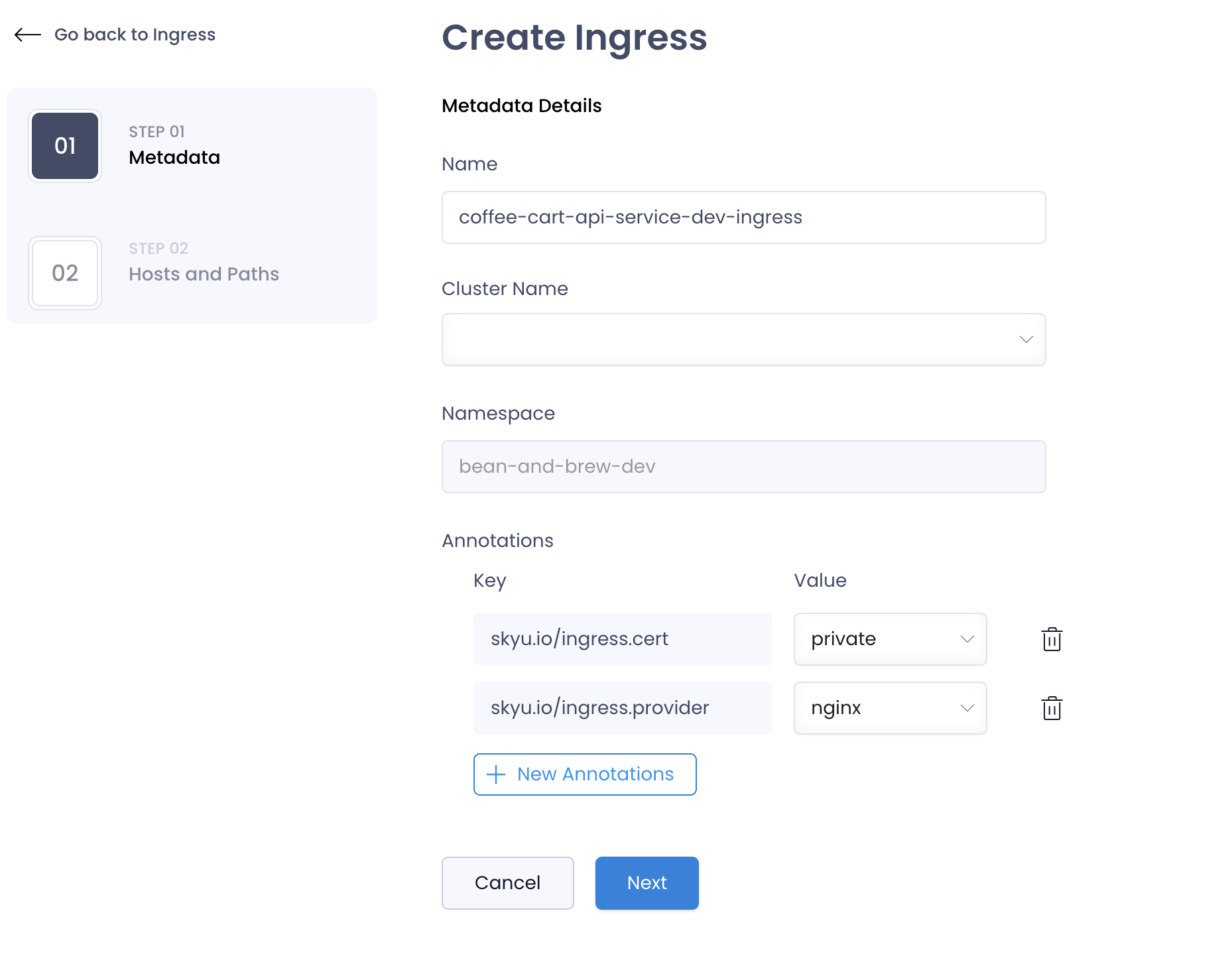
You can create an Ingress by clicking on the Create Ingress button under specific Kubernetes environment inside an application in the SkyU Console.
Metadata Details
In the metadata section, you can provide the following details:
| Field | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Name | Name of the Ingress. This has to be unique across your organization and should not contain special characters. | test-ingress |
| Namespace | Select the namespace where the Ingress should be created. | default |
| Cluster | Select the cluster where the Ingress should be created. | docker-desktop |
| Annotations | Add annotations to the Ingress. This is used for adding metadata to the Ingress. |
Annotations
Annotations are key-value pairs that can be used to specify non-identifying metadata about objects. They can be used to store information that is not part of the object definition.
Skyu supports the following annotations for Ingress:
skyu.io/ingress.cert: This annotation is used to specify the certificate for the Ingress. These are the expected values for the annotation:private: This annotation is used to specify that the Ingress should be secured with a custom certificate user has manually made.cert-manager: This annotation is used to specify that the Ingress should be secured with a cert-manager certificate. If this is chosen, the user should provide the cert-manager issuer name in theskyu.io/ingress.cert.issuerannotation.none: This annotation is used to specify that the Ingress should not be secured with a certificate.
skyu.io/ingress.provider: This annotation is used to specify the Ingress provider. These are the expected values for the annotation:nginx: This annotation is used to specify that the Ingress should be created with the NGINX Ingress Controller.traefik: This annotation is used to specify that the Ingress should be created with the Traefik Ingress Controller.
You can add any additional ingress annotations in the Annotations field.
Hosts and Paths
In the Hosts and Paths section, you can provide the following details:
| Field | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Select DNS | You can register a wildcard or a DNS in SkyU Clusters. Read more in Cluster DNS section | |
| Host | The host name of the Ingress. This is the domain name that the Ingress will route traffic to. | test.com |
| Path | The path of the Ingress. This is the path that the Ingress will route traffic to. | / |
| Service Port | The port of the service that the Ingress will route traffic to. | 80 |
TLS
If you enable TLS, provide the secret name that contains the certificate and key for the Ingress. The secret must be created in the same namespace as the Ingress.
If you are using cert-manager, you don't need to create a secret manually. Cert-manager will create the secret for you. Just give a name for the secret
Common Ingress Use Cases
NGINX Ingress Controller
Multi Service Routing
Ingress can be used to route traffic to multiple services based on the host name and path. You can create multiple rules in the Ingress to route traffic to different services based on the host name and path.
Here are the annotations you can use to create an Ingress with NGINX Ingress Controller:
| Annotation | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target | The value of this annotation is a regular expression that will be used to rewrite the URL. The Ingress controller will rewrite the URL based on the regular expression. | /$2 |
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/use-regex | This annotation is used to specify that the rewrite-target annotation should be treated as a regular expression. | 'true' |
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/permanent-redirect-code | This annotation is used to specify the HTTP status code for permanent redirect. | 301 |
Once these annotations are added, you can create multiple rules in the Ingress to route traffic to different services based on the host name and path.
if you have a service running on the path /service1 and another service running on the path /service2, you can create an Ingress with the following rules:
Path Type: ImplementationSpecific
Path: /service1(/|$)(.*)
Service Name: service1
Service Port: 80 Path Type: ImplementationSpecific
Path: /service2(/|$)(.*)
Service Name: service2
Service Port: 80WebSocket Support
Ingress can be used to route WebSocket traffic to services. You can create an Ingress with the following annotations to enable WebSocket support:
| Annotation | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/websocket-services | This annotation is used to specify the services that should be treated as WebSocket services. | service1 |
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-read-timeout | This annotation is used to specify the timeout for reading a response from the proxied server. | 3600 |
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-send-timeout | This annotation is used to specify the timeout for sending a request to the proxied server. | 3600 |
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-connect-timeout | This annotation is used to specify the timeout for establishing a connection with the proxied server. | 3600 |
Handle Large Request Body
Ingress can be used to handle large request bodies. You can create an Ingress with the following annotations to handle large request bodies:
| Annotation | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-body-size | This annotation is used to specify the maximum size of the request body that the server can accept. | 500m |
SSL Passthrough
Sometimes, you may want to route SSL traffic to the services directly. This means you will be mounting certificates directly inside your container. You can create an Ingress with the following annotation to route SSL traffic to the services directly:
| Annotation | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-passthrough | This annotation is used to specify that the Ingress should route SSL traffic to the services directly. | true |
AWS ALB Ingress Controller
Websocket Suppprt
Ingress can be used to route WebSocket traffic to services. You can create an Ingress with the following annotations to enable WebSocket support:
| Annotation | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/target-type | This annotation is used to specify the target type for the ALB. | ip |
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/listen-ports | This annotation is used to specify the ports that the ALB should listen on. | [{"HTTPS": 443}] |
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/target-group-attributes | This annotation is used to specify the target group attributes for the ALB. | stickiness.enabled=true,stickiness.lb_cookie.duration_seconds=60 |
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/load-balancer-attributes | This annotation is used to specify the load balancer attributes for the ALB. | idle_timeout.timeout_seconds=600 |